Qatar’s Climate: Weather, Seasons, and Climate Change
Qatar’s climate is shaped by its location in the Arabian Peninsula, where desert conditions dominate the landscape. The country experiences some of the hottest summers in the world, mild winters, and very little rainfall throughout the year. These climatic conditions not only influence daily life but also affect Qatar’s economy, tourism, sports, and even urban planning.
Spring in Qatar (March – May) Overview
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Rises from around 20°C in March to 30°C by May |
| Rainfall | End of the cooler season’s showers |
| Sunshine | 11.5 to 13.5 hours of daylight |
Outdoor Activities
| Activity Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Water Sports | Kayaking and paddleboarding at Al Thakira mangroves |
| Coastal Exploration | Kite surfing at Fuwariat Beach, walking along Doha Corniche |
| Nature Walks | Desert wildflowers blooming, perfect for walks and photography |
Cultural & Indoor Activities
| Activity Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Cultural Exploration | Katara Cultural Village – art, events, exhibitions |
| Seasonal Events | Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr, Ajyal Film Festival (depending on year) |
| Shopping | World-class malls and traditional souqs |
Tips for Visitors
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Stay Hydrated | Drink plenty of water throughout the day |
| Sun Protection | Use sunscreen, wear light long-sleeved clothes, avoid 10:00 – 16:00 direct sun |
| Dress Comfortably | Switch from boots to sandals or flip-flops as temperatures rise |
Understanding Qatar’s climate is essential for travelers, researchers, and policymakers. From its ancient maritime heritage to its modern development, Qatar has always adapted to its harsh natural environment. This article provides a complete overview of Qatar’s climate facts, weather patterns, climate change challenges, and lifestyle impact, making it a valuable guide for anyone interested in the country’s environment.
Overview of Qatar’s Climate
Qatar’s Climate Overview
| Season | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Summer (May–September) | – Extremely hot and dry, often exceeding 45°C (113°F). – High humidity in coastal areas, especially June–September. – Almost no rainfall. |
| Winter (December–February) | – Mild and pleasant, averaging 20–25°C (68–77°F). – Most annual rainfall occurs between October–March. |
| Spring & Fall (April, May, October, November) | – Temperatures average 17–25°C (63–77°F). – Comfortable and ideal for outdoor activities. |
Other Climate Factors
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Sand & Dust Storms | Caused by Shamal winds, occurring at different times of the year. |
| Extreme Temperatures | Qatar experiences some of the world’s highest recorded temperatures, with a record of 50.4°C (122.7°F) in July 2010. |
Qatar has a hot desert climate, also referred to as arid or hyper-arid. The summers are long, hot, and humid, while winters are short and relatively mild. Rainfall is very low, averaging less than 100 millimeters annually, and is mostly confined to the cooler months of December through March.
- Qatar’s climate facts:
- Average summer temperatures: 40–45°C (104–113°F)
- Winter temperatures: 15–24°C (59–75°F)
- Annual rainfall: 80–100 mm, mainly in short bursts
- Frequent dust storms caused by northwesterly winds (shamal)
- Average summer temperatures: 40–45°C (104–113°F)
- Qatar’s climate Wikipedia page highlights the country as one of the hottest places on Earth.
- Qatar’s climate map reveals the prevalence of desert conditions, with slight variations in coastal humidity and inland dryness.
The lack of natural rivers and lakes, combined with high evaporation rates, results in scarce water resources, making desalination plants essential for survival.
🌤️ Weather in Qatar
| Month | Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Temp (°C) | 35° | 32° | 25° | 22° | 23° | 27° | 32° | 32° | 41° | 41° | 41° | 39° |
| Min Temp (°C) | 23° | 23° | 15° | 13° | 14° | 17° | 21° | 21° | 28° | 29° | 29° | 26° |
| Rainfall (mm) | 1.1 | 3.3 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 17.1 | 16.1 | 8.7 | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Data source: QatarBestPlaces | Climate overview for winter and summer months.
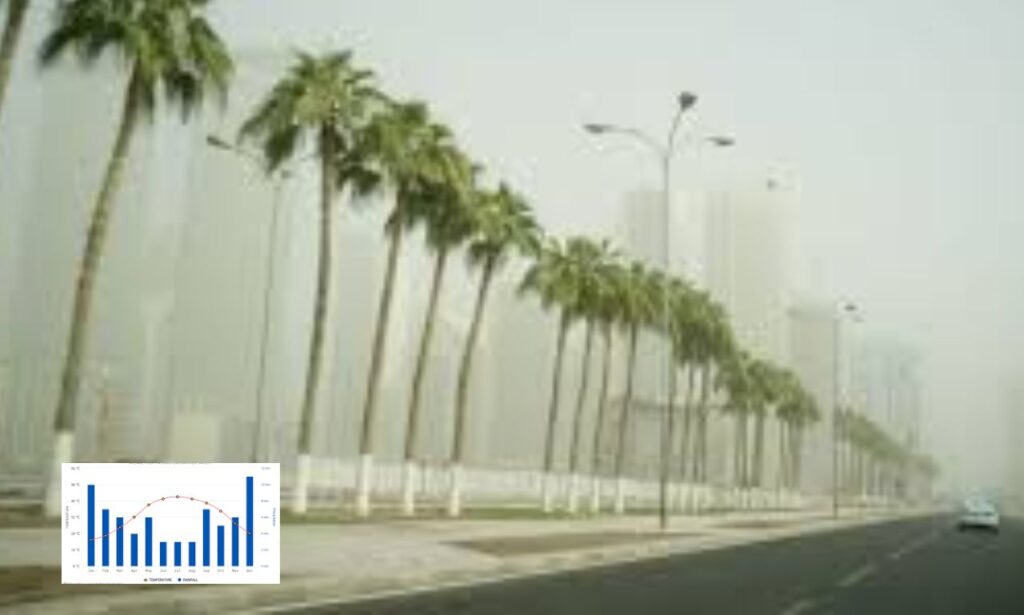

Qatar’s Weather by Season
Summer (June–September)
Summer in Qatar is extremely hot and humid, often unbearable without air conditioning. Temperatures can exceed 45°C (113°F) and sometimes approach 50°C (122°F). Coastal regions such as Doha experience intense humidity, making the heat feel even more suffocating.
- Outdoor activities are limited, and most residents avoid direct sunlight during the midday hours.
- Dust storms are common in July and August, affecting air quality.
- Workers’ schedules, especially for outdoor labor, are often adjusted to avoid peak heat hours.
This explains why the Qatar climate by month graphs show consistent spikes in summer temperatures.
Winter (December–February)
Winter is the most pleasant season in Qatar. The weather becomes mild and enjoyable, attracting tourists and making it the preferred time for outdoor festivals and sports events.
- Qatar climate in December: Average highs are around 24°C (75°F), with cooler evenings.
- Occasional rainfall may occur, though it is brief and irregular.
- Parks, beaches, and desert safari tours are particularly popular in this season.
For travelers, the months of December to February are the best time to visit, as the weather is comfortable for sightseeing and cultural activities.
Spring (March–May) & Autumn (October–November)
Spring and autumn are transitional seasons in Qatar.
- Spring (March–May): Warm days with average highs of 30–35°C (86–95°F). Occasional showers are expected in March.
- Autumn (October–November): Marked by cooler evenings and highs of around 28–33°C. This period signals the beginning of Qatar’s peak tourist season.
Both seasons provide relatively bearable temperatures, making them favorable for outdoor events and travel. Many visitors consult Qatar’s climate graphs to decide between spring and autumn travel dates.
Current & Weekly Weather
Qatar’s desert climate means that day-to-day changes are minimal, but short-term variations occur due to humidity and wind.
- Qatar’s climate today: Hot, dry, and clear skies are the norm. Coastal humidity may rise significantly in summer.
- Qatar’s climate tomorrow: Similar patterns continue, though dust storms or humidity shifts may cause variations.
- Qatar’s climate this week: Predictable heat dominates, with slightly cooler evenings in the winter months.
👉 Note: For live updates, always consult the Qatar Meteorology Department or reliable weather apps, as conditions like dust storms can affect visibility and health.
Climate Change in Qatar
Qatar, like other Gulf countries, is facing the growing threat of climate change. Rising global temperatures are causing:
- Longer and hotter summers
- Increased frequency of dust storms
- Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities like Doha
- Water scarcity and higher demand for desalination
The government has launched the Qatar Climate Change Strategy, which includes:
- Reducing carbon emissions through renewable energy projects
- Expanding solar energy capacity
- Developing eco-friendly public transportation
- Building climate-resilient infrastructure
According to Qatar Climate News, major initiatives, such as hosting the carbon-neutral FIFA World Cup 2022, have demonstrated Qatar’s efforts to balance global leadership with climate responsibility.
Historical Climate Data
Climate records confirm that Qatar has been experiencing increasingly hot summers in recent decades.
- Qatar’s climate trends in 2021 & 2022: Both years reported record highs, with temperatures exceeding 50°C.
- Rainfall remained scarce, with only sporadic showers.
- Heat stress has become a growing issue for both residents and migrant workers.
Climate graphs produced by international agencies for Qatar show a steady upward trend in average annual temperatures. These graphs illustrate how Qatar’s climate has become increasingly harsh, underscoring the urgency of climate adaptation.
Qatar Weather Tips
Get our handy tips to enjoy a cool and comfortable stay in Qatar.
- ☀️ Stay hydrated: Always carry water with you, especially during outdoor activities.
- 🧴 Use sunscreen: Apply SPF 30+ and wear sunglasses to protect against strong UV rays.
- 👕 Wear light clothing: Choose loose, breathable fabrics like cotton and linen.
- 🌇 Plan outdoor trips early or late: Avoid the midday heat (11 AM – 3 PM).
- 🏖 Enjoy the evenings: Visit beaches or souqs after sunset for cooler temperatures.
Climate and Lifestyle in Qatar
Qatar’s climate directly shapes its population distribution, economy, and lifestyle.
- Population: Most of Qatar’s 2.7 million residents live in Doha and coastal areas, where infrastructure supports daily life in extreme weather.
- Economy: The country has invested heavily in cooling systems, indoor facilities, and energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Tourism: Visitors prefer winter months, when outdoor festivals, desert safaris, and cultural events are most enjoyable.
- Sports: Climate significantly influenced the FIFA World Cup 2022, which was scheduled for November–December to avoid the extreme summer heat. Cooling technologies inside stadiums showcased Qatar’s innovation.
Even traditional practices such as pearling and fishing were historically influenced by Qatar’s maritime climate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Qatar’s climate?
Qatar has a desert climate with hot summers, mild winters, and plenty of sunshine throughout the year.
What is the best time of year to visit for warm-weather activities?
The best time to visit Qatar is between November and April, when the weather is pleasant and ideal for outdoor adventures.
Which areas of Qatar are the coolest?
Coastal regions like Al Wakrah and Al Khor tend to be slightly cooler due to sea breezes, especially during the evenings.
Is Qatar very humid?
Yes, humidity levels can be high, particularly in coastal areas during the summer months of July and August.
Does it rain a lot in Qatar?
No, rainfall is minimal. Most rain occurs between December and March, often in short bursts.
What is the coldest month in Qatar?
January is typically the coldest month, with daytime temperatures around 20°C and cooler nights.
Are there any extreme weather conditions in Qatar?
Occasionally, Qatar experiences dust storms during spring and early summer, but severe weather events are rare.
FAQs
Q1: What is the climate like in Qatar?
Qatar has a hot desert climate, characterized by scorching summers, mild winters, and very little rainfall.
Q2: Is Qatar hot all year round?
Yes, Qatar is hot throughout the year, though winters (December–February) are mild and enjoyable.
Q3: Does Qatar have winter?
Yes, but it is short and mild, with temperatures ranging from 15°C to –24°C.
Q4: What month is best to visit Qatar?
November to March is the best time, when the weather is pleasant for outdoor activities.
Q5: How is Qatar dealing with climate change?
Qatar is implementing renewable energy projects, sustainable development initiatives, and climate adaptation strategies.
Conclusion
Qatar’s climate is one of the most defining aspects of the country’s identity. The hot desert conditions have shaped its history, culture, economy, and modern infrastructure. From managing extreme summer heat to adopting strategies against climate change, Qatar demonstrates resilience and innovation in the face of environmental challenges.
For travelers, the country offers an incredible experience, particularly during the cooler months from November to March. For policymakers, Qatar’s environmental strategies serve as a model for how nations can adapt to a warming world.
As the country continues to balance tradition with modernization, understanding Qatar’s climate remains key to appreciating its unique way of life.