History of Qatar: Timeline, Culture, and Key Facts
Before 1971, the area now known as Qatar was referred to as the Qatari Peninsula. It had previously been part of the Ottoman Empire in the late 19th century and later came under British control as a protectorate. However, the region’s more modern history can be traced back to early settlements such as Al-Zubārah in the 18th century.
A summary of Qatar’s status before 1971:
- Ottoman Influence: In the late 19th century, the territory was under Ottoman control and influence.
- British Protectorate: Following the decline of Ottoman rule, Qatar became a British protectorate after the 1916 Anglo-Qatari Treaty, which safeguarded it from external interference.
- Geographic Reference: The land did not have another official country name; it was commonly referred to simply as the Qatari Peninsula.
History of Qatar: Timeline
-
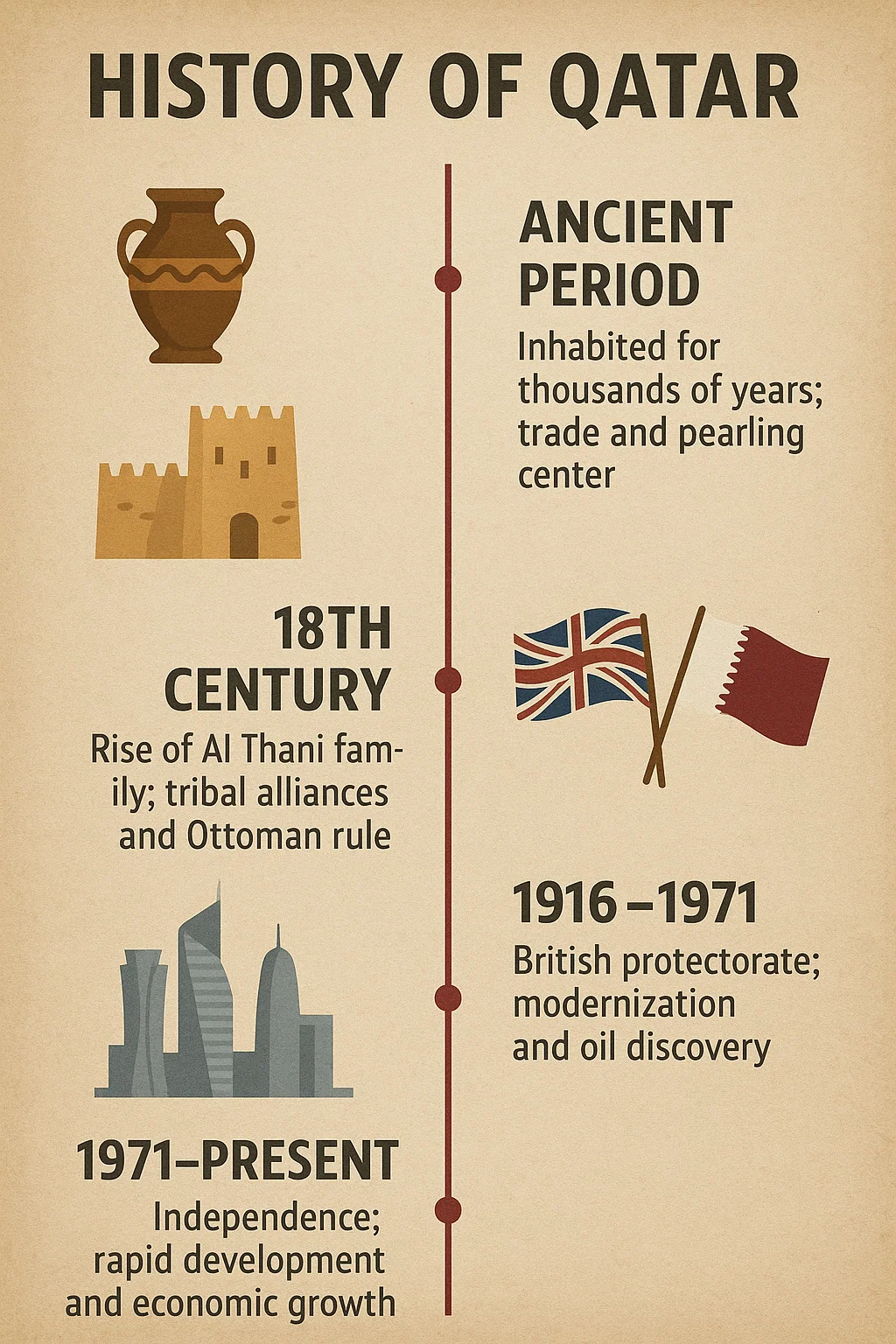
Prehistory (6000–4000 BCE)
Earliest human settlements, stone tools, Ubaid period coastal life.
-
8th–9th Century
Pearl diving and fishing become the main livelihood.
-
18th Century
Al Thani family emerges, Al Zubarah becomes a trading hub.
-
1868
Treaty with Britain recognizes Qatar’s leadership.
-
1871–1913
Ottoman influence, but Al Thani maintains autonomy.
-
1935–1949
Oil concessions, discovery & start of oil production.
-
1971
Qatar gains independence from Britain (3 Sept 1971).
-
1995
Modernization begins under Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani.
-
2017–2021
Gulf blockade; Qatar develops new alliances.
-
2022
Qatar hosts FIFA World Cup – first in Middle East.

ancient history of qatar
For centuries, Qatar’s survival depended on the sea and its strategic position in the Gulf. The country was shaped by pearling, trade, and regional struggles between empires. On 3 September 1971, Qatar declared independence, stepping away from British protection and entering the modern era as a sovereign state. Since then, it has transformed dramatically, with a booming economy, thriving aviation sector, and cultural projects that connect past and present.
This article presents a comprehensive history of Qatar, covering its ancient roots, independence, modern growth, culture, geography, symbols, and achievements. It also provides resources such as a history of Qatar PDF, book references like Masters of the Pearl: A History of Qatar, and answers to common questions like “What was Qatar called before 1971?” and “When was Qatar discovered?”
Ancient History of Qatar
The ancient history of Qatar stretches back thousands of years. Archaeological evidence reveals settlements along the coast that depended heavily on the sea. Qatar’s maritime history and heritage remain central to its identity.
- Early settlements: Archaeological digs at sites like Al Zubarah show evidence of pottery, coins, and stone tools dating back centuries.
- Pearling and fishing: The Gulf waters were rich with natural pearl beds. By the 18th and 19th centuries, Qatar’s pearls were traded as far as Europe and India.
- Trade connections: Due to its strategic location, Qatar served as a hub for trade routes between Mesopotamia, Persia, and the Indus Valley.
Even before oil, Qatar’s economy and culture revolved around the sea. The hardship of desert life combined with seafaring resilience shaped Qatari traditions.

Qatar Before Independence
What was Qatar called before 1971?
Historical records, including Ptolemaic maps, refer to the peninsula as “Qatara”. Over centuries, this evolved into Qatar.
Ottoman and British Influence
In the 19th century, Qatar came under Ottoman rule, though its presence was limited. By 1916, Britain established Qatar as a protectorate, controlling its foreign affairs while the Al Thani family managed domestic governance.
Pearl Trade Economy
From the 18th to the early 20th century, the pearl trade was Qatar’s lifeline. Almost every family depended on pearling, either as divers, sailors, or traders. However, the global collapse of the pearl market in the 1930s, caused by Japanese cultured pearls and the Great Depression, devastated Qatar’s economy.
Transition to Oil
In 1939, oil was discovered at Dukhan, marking a major shift. Though exports began after World War II, oil revenues slowly changed Qatar’s economic structure, laying the groundwork for independence.
Independence and Modern History

When was Qatar discovered?
Arab sailors and merchants knew of Qatar for centuries, but European explorers formally documented it in the 1500s due to its pearl wealth.
Independence in 1971
On 3 September 1971, Qatar declared independence from Britain, becoming the State of Qatar. Sheikh Khalifa bin Hamad Al Thani became Emir, guiding the nation through its first steps as a sovereign country.
Modern History of Qatar
Post-independence, Qatar quickly transitioned into a modern state.
- Political system: A constitutional monarchy led by the Al Thani family.
- Economic boom: Oil and natural gas exports placed Qatar among the wealthiest nations per capita.
- Global influence: Qatar invested in education, culture, and sports diplomacy.
- FIFA World Cup 2022: Hosting the tournament elevated Qatar’s international profile.
The modern history of Qatar shows how a small desert peninsula became a global economic and cultural leader within a few decades.
Culture and Royal Family
History of the Qatar Royal Family
The Al Thani dynasty has ruled Qatar since the mid-19th century. Sheikh Mohammed bin Thani consolidated power and paved the way for independence. Today, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani is Emir, with Mohammed bin Abdulrahman bin Jassim Al Thani serving as Prime Minister.
History and Culture of Qatar
The history and culture of Qatar are tied to Bedouin traditions, Islamic faith, and maritime heritage.
- Religion: Islam is the state religion.
- Language: Arabic is the official language; English is widely spoken.
- Traditions: Falconry, dhow sailing, and majlis gatherings remain integral.
- Qatar population: Around 2.7 million (2023), with only ~12% native Qataris, the rest expatriates.
Qatar’s identity is shaped by a mix of tradition and openness to global cultures.
Symbols and National Identity
History of the Qatar Flag
Qatar’s flag is maroon with nine white serrated edges, symbolizing unity and independence. Its unique color distinguishes it from other Gulf nations.
History of Qatar National Day
Celebrated annually on 18 December, it honors Sheikh Jassim bin Mohammed Al Thani, who unified the nation in 1878.
History of the National Museum of Qatar
The museum, designed like a desert rose by architect Jean Nouvel, opened in 2019. It preserves Qatar’s history, culture, and heritage while symbolizing its modern vision.
These symbols strengthen the sense of unity among citizens and reflect national pride.
Qatar Airways and Modern Growth
History of Qatar Airways
Launched in 1993, Qatar Airways transformed from a small regional airline into a global leader.
- Flies to over 160 destinations.
- Consistently ranks among the top airlines in the world.
- Helped make Doha a global aviation hub.
Crash History of Qatar Airways
While searches for the crash history of Qatar Airways exist, the airline maintains an exceptional safety record, with no fatal passenger crashes.
The success of Qatar Airways reflects the nation’s broader ambition to position itself as a connector between continents.
Geography of Qatar
Natural Geography and Features
- Location: Northeastern Arabian Peninsula.
- Land area: ~11,500 sq. km.
- Geographical features: Flat desert terrain, limestone plateaus, and coastal plains.
- Does Qatar have mountains? No — the land is mostly flat.
- Climate: Hot desert climate with mild winters.
- Natural features: Desert dunes, mangroves, and marine life.
Cities and Population
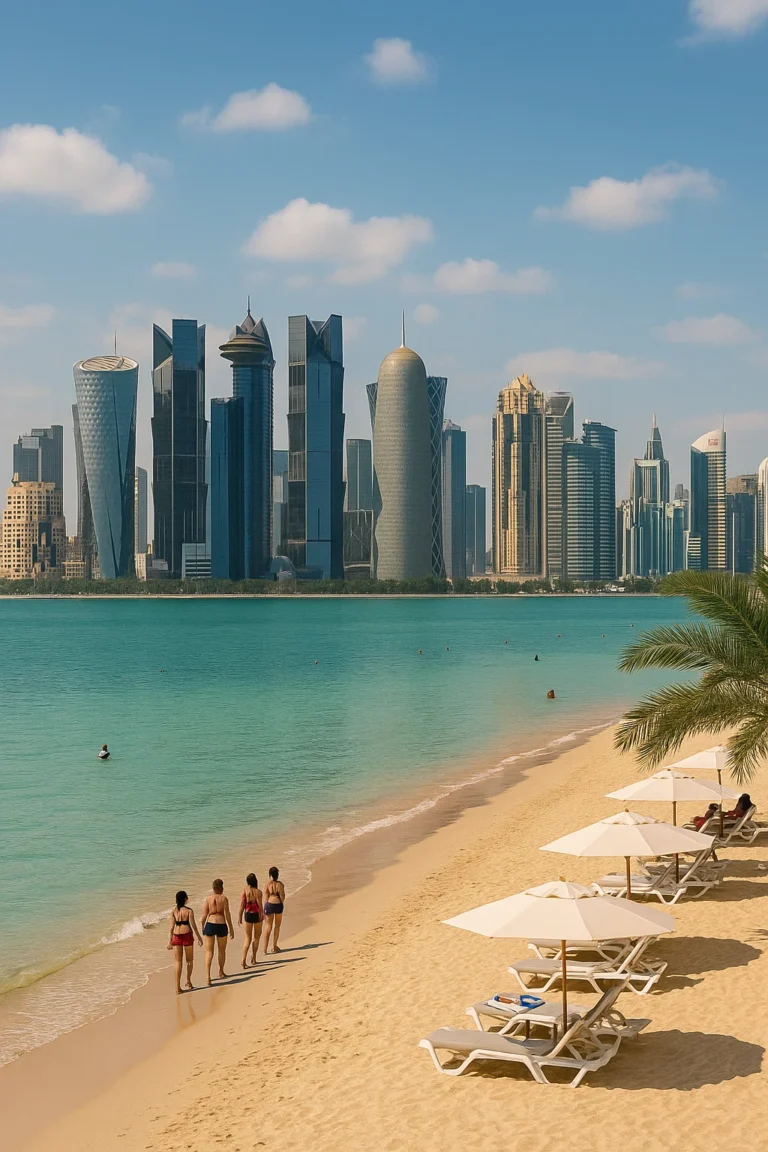
- Capital of Qatar: Doha.
- Main cities: Al Wakrah, Ar-Rayyan, Umm Salal, Al Khawr.
- Qatar population: ~2.7 million (2023).
FAQs on Geography
- Is Qatar located in Dubai?
- No, Qatar is an independent state; Dubai is part of the UAE.
- Is Qatar safe?
- Yes, Qatar is one of the safest countries in the Middle East.
- Map of Qatar and surrounding countries:
- Shows its position between Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and the UAE.
The geography of Qatar shaped its history, economy, and role as a maritime hub.
Economy and Development
The Qatar economy is driven by oil and natural gas, making it one of the wealthiest countries globally.
- Qatar holds the world’s third-largest natural gas reserves.
- LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) exports are central to its wealth.
- Investments in sports, real estate, and education diversify the economy.
Qatar’s rapid development is an example of how resource wealth can transform a nation within a few decades.
Books and Resources
For deeper study, resources include:
- Masters of the Pearl: A History of Qatar – Michael Quentin Morton.
- History of Qatar Wikipedia.
- History of Qatar PDF downloads.
- Resources in multiple languages: History of Qatar in English, Hindi, and Urdu.
- Official sources: History of Qatar | The Amiri Diwan and History of Qatar | People, Flag, Culture, & Facts.
Timeline of Qatar’s History
- Ancient era: Early settlements, pearling, trade.
- 18th century: The Al Thani dynasty rises.
- 1916: Qatar becomes a British protectorate.
- 1930s: Collapse of the pearling industry.
- 1939: Oil was discovered at Dukhan.
- 1940s–60s: Oil revenues drive modernization.
- 1971: Independence declared on 3 September.
- 1993: Qatar Airways was founded.
- 2000s: LNG boom, global diplomacy.
- 2010: Wins FIFA World Cup hosting rights.
- 2022: Hosts FIFA World Cup.
The history of Qatar timeline shows its dramatic transformation.
History of Qatar
The peninsular state of Qatar shows evidence of habitation over millennia, evolving into a modern nation under the leadership of the Al Thani family.
All tribes unite under the rule of the Al Thani family, paving the way for stability and regional independence.
Sheikh Mohammed bin Thani signs an agreement with the British authorities, recognizing Qatar as an independent entity.
Qatar maintains autonomy under Ottoman control, guided by Sheikh Jassim bin Mohammed Al Thani until his death in 1913.
Sheikh Abdullah bin Jassim Al Thani signs the Anglo-Qatari Treaty, safeguarding Qatar’s sovereignty.
Qatar signs its first oil-prospecting agreement with the Anglo-Persian Oil Company, marking a new economic era.
Oil is discovered, but exploration halts during World War II until exports begin in the 1950s.
Qatar joins global organizations such as UNESCO and WHO, expanding its international presence.
Britain announces its withdrawal from the Gulf, setting the stage for Qatar’s independence.
HH Sheikh Khalifa bin Hamad Al Thani declares the dissolution of the 1916 Treaty, officially establishing the State of Qatar.
FAQs about Qatar’s History
Q1: What is the old name of Qatar?
It was called Qatara in ancient maps.
Q2: When was Qatar discovered?
Europeans documented it in the 1500s, though Arabs had long known the region.
Q3: What are five facts about Qatar?
- Highest GDP per capita globally.
- The Al Thani family has ruled for 150+ years.
- Qatar Airways is among the world’s top airlines.
- Qatar hosted the FIFA World Cup 2022.
- The Qatar population is mostly expatriates.
Q4: What made Qatar famous?
Pearling, oil and gas wealth, cultural diplomacy, and international sports.
Q5: Is Qatar safe?
Yes, it is among the safest countries in the Gulf.
Geography of Qatar
Qatar is a country of striking geographical contrasts, from crescent-shaped dunes to a serene coastline of beaches and islands. Learn more about its mix of ultra-modern cities like our capital city of Doha, ancient villages and natural wonders.
Conclusion
The history of Qatar is a story of resilience, cultural pride, and transformation. From ancient maritime traditions and pearling to the discovery of oil and independence in 1971, Qatar has risen to become a global leader in energy, culture, and sports.
Its identity is shaped by the Al Thani royal family, its Islamic and Bedouin traditions, and its modern vision for progress. With a dynamic economy, global connections through Qatar Airways, and cultural landmarks like the National Museum of Qatar, the State of Qatar continues to shape its destiny while preserving its heritage.
Today, Qatar represents not only a timeline of history but also a symbol of ambition, resilience, and achievement in the heart of the Middle East.